The present simple tense is the most frequently used and most well-known tense. It is also referred to as the simple present or simple indefinite.
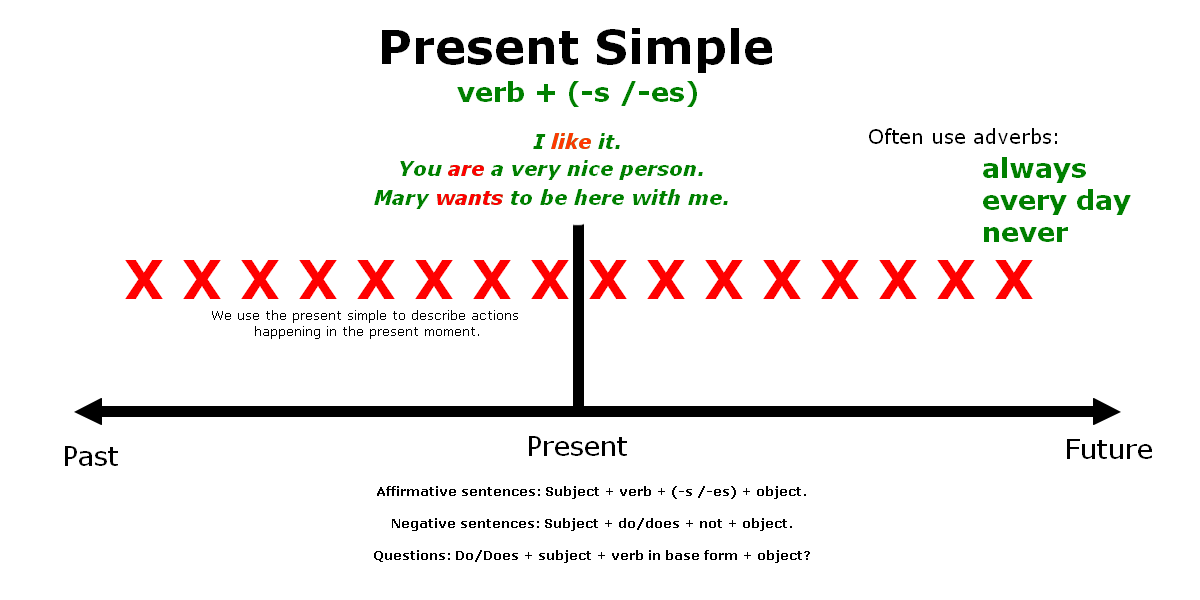
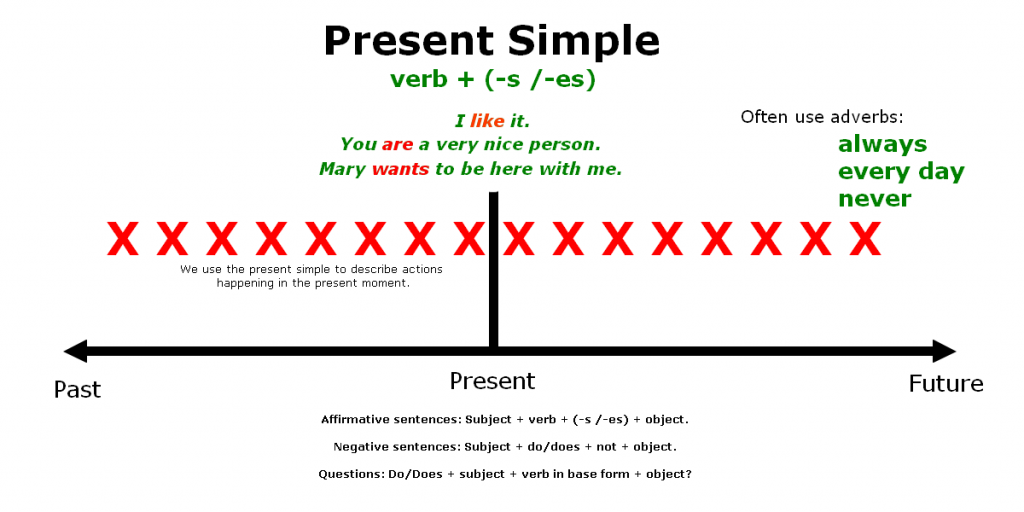
We use the present simple to describe actions happening in the present moment, either if the action is happening right now or if it happens repeatedly. We also call this tense the present indefinite because it is used to talk about actions that happen unceasingly.
In the present simple tense, we add the suffix –s /-es to the main verb depending on the person in the subject. An interesting fact is that the present simple tense is the most used verb form in English and is used in 50% of the spoken language.
See also:
- Present simple tense examples
- 5 sentences of simple present tense
- 10 sentences of simple present tense
- 20 sentences of simple present tense
- 100 sentences of simple present tense
- Present Simple tense Questions
- Present Simple tense Negative sentences
- Simple present tense structure and examples
Why is the present simple tense called simple?
This tense is called simple because the base form of the main verb is a single word (feel –> feels). In comparison with other present tenses, the present simple really is simple.
On the other hand, the present continuous tense (is feeling) and present perfect (has liked) are tenses with more than just one main verb (each consisting of a minimum of two main verbs).
Another reason why this tense is called simple is because all the verbs in the present simple are in dictionary form. The only exception is when the subject of the sentence is in the 3rd person – then we add the suffix – s/es.
The verb „to be“
The verb „to be“ is one of the verbs that have a special form in the present simple. This verb and a few others are special because we use their irregular form (present tense). The verb „to be“ is probably the most important one of them all.
We use its forms: „am“, „are“ or „is“.
Using irregular forms of the verb „to be“
Using irregular forms of the verb „to be“ in the present simple depends on the person of the subject. There are some rules that exist for using these forms.
Irregular form „Am“
We use the form „am“ in combination with the 1st person singular (I am). We can use also its short-form (I’m).
Example:
- I am really hungry.
- I’m so much happier right now.
Irregular form „is“
This form of the verb „to be“ is only used in combination with the 3rd person singular (he, she or it). We also very often use its short-form (‘s), apostrophe included.
The short-form looks like:
He is –> He’s, She is –> She’s, It is –> It’s
Example:
- He is a clever guy.
- She is awesome.
- It’s stupid.
Irregular form „are“
We use this form if we talk about the 2nd person singular (you) or any person in plural form (we, you, they). We can also use its short-form (‘re), apostrophe included. The short-forms look like:
We are –> We’re, You are –> You’re, They are –> They’re
Example:
- You are really cute.
- They’re at school.
- We are just like them.
The verb „do“
We use the verb „do“ in many ways in the present simple tense. We can use it to describe that we are doing something, but we can also use it to construct entire sentences. The main purpose of this verb in the present simple is in forming questions. When we are constructing questions, we almost always start with the verb „Do/Does“.
When do we use „do/does“?
We use „do/does“ depending on the person in the subject. We must remember that we have to distinguish between subjects in questions. A big mistake that happens is when we switch a verb with a subject. We have to memorize when to use „do“ and when to use „does“.
Do
We use the verb form „do“ for every person in the subject except for the 3rd person singular. This means we use the verb „do“ in combination with I, You, We and They.
Example:
- Do you feel that?
- Do they eat mushrooms?
Does
The form „does“ is only used in the 3rd person singular – we do not use it in any other way. This means we only use the verb „does“ in combination with subjects He, She or It.
Example:
- Does she like it?
- Does Jamie live in London?
The verb „have“
The verb „have“ is another special verb in the present simple tense whose irregular forms (also a present tense) we use, which are „have“ or „has“. When do we use either „have“ or „has“?
Form „has“
The form „has“ is used with the 3rd person singular (He, she, it).
Example:
- He has really nice eyes.
- She has got a nice t-shirt.
Form „have“
We use this form in combination with all persons, except for the 3rd person singular.
Example:
- We have got all the money.
- You have a stain on your sweater.
When do we use the present simple tense?
We use the present simple tense on many occasions. Because this tense is the most common tense, there are really many ways to use it. We use the present simple to talk about:
Something that is true right now (in the present time)
We use this tense to describe some action or fact that is happening right now. We use it very often to talk about age, place of living, relationships or events that last a long time in the present.
Example:
- I am 18 years old.
- She is a student.
- They live in Paris.
- We love pizzas, especially the homemade ones.
Something happening repeatedly in the present
This tense is also used to describe actions happening regularly in the present as well as to talk about habits, repeated actions or other situations. We frequently use adverbs like „always“, „every day“, „never,“ and others when describing repetitive situations.
Example:
- I play basketball every weekend at 5 o’clock.
- We always add chilli to this soup.
Something that is always true
This tense is also used to talk about things that are and will always be true. These can be some facts about physics or something that everybody knows to be true and which will always be true, no matter what.
Example:
- The human body contains about 60 % water.
- Trees are green.
- The sun is about 6000 °C.
Stative verbs and verbs of thought
We use the present simple tense to talk about thoughts or feelings, or in combination with stative verbs (verbs which we cannot combine with the suffix –ing). We use very often adverbs like like, love, hate, think, as well as others.
Example:
- Terry likes rugby.
- He is not really smart.
Future actions/events that are predetermined
These are things like schedules, bus timetables or any kind of programme.
Example:
- The bus to London leaves at 16:46 AM.
- The party starts at half past the hour.
Construction of sentences
Constructing sentences in the present simple tense is not hard. The only thing we have to remember is to add the suffix –s/es/ies to verbs in sentences with the 3rd person singular. Another useful piece of information is to know how to use the verb „do/does“ in questions as well as in negative sentences.
Affirmative sentence
The affirmative present simple is made from a verb in base form with a subject and object. We have to know whether the subject is in 3rd person singular (he, she or it) or not, as we would need to add the suffix –s/es to the base verb when the 3rd person singular is used.
The sentence will look like:
Subject + verb + (-s /-es) + object.
Example:
- I like it.
- She loves sushi.
- Mary wants to be here with me.
- You are a very nice person.
Negative sentence
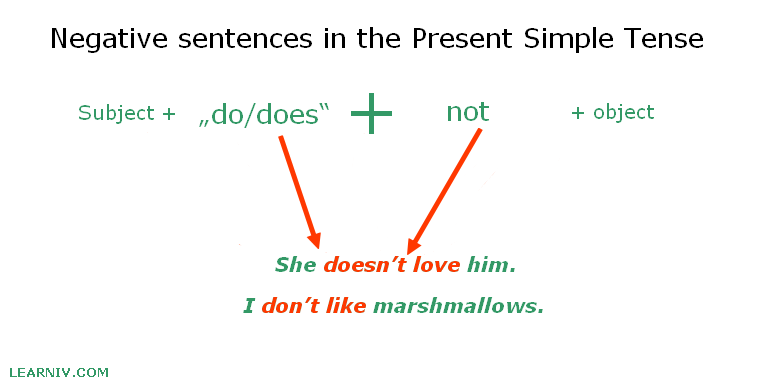
The negative meaning of a sentence in the present simple tense is easy to construct. While in affirmative sentences we have to think about the person of subject and add a specific suffix, in negative sentences we do not add anything. We simply use the correct form of the verb „do“ depending on the person of the subject.
We construct a negative sentence by adding the word „not“ after the verb „do/does“.
If we talk about the 3rd person singular, we use the verb „does not/doesn‘t“. If we talk about any other person, we always use „do not/don‘t“.
The important thing to note here is that we do not combine a suffix with the verb „does“.
We cannot construct a sentence like the following: „He does not likes bananas,“. Instead, we only use the verb in its base form instead of combining it with a suffix, as we do in affirmative sentences. The correct sentence will be: „He does not like bananas.“
The sentence will look like:
Subject + do/does + not + object.
Examples:
- She doesn’t love him.
- I don’t like marshmallows.
- We do not go there.
Questions in the present simple
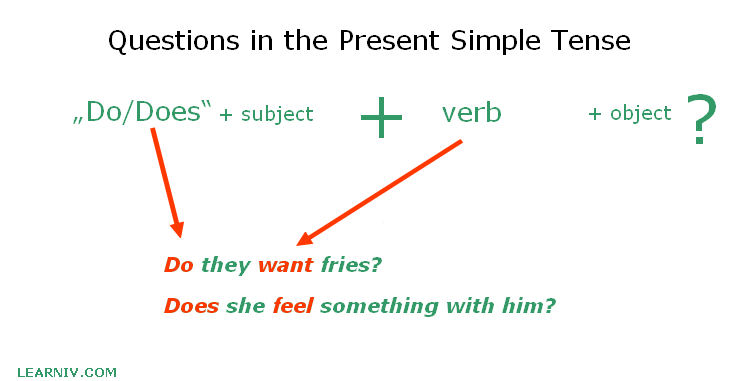
Constructing questions in the present simple tense is really easy. The only thing we have to know is that we have to start the whole sentence with the verb „do“ or „does“.
The sentence will look like:
Do/Does + subject + verb in base form + object?
The important thing to note here is that we do not add the suffix –s/-es to the 3rd person singular in questions. If we add the auxiliary verb „does“ to the beginning of the question, it automatically means we do not have to add any suffix to the main verb. As such, we always use the verb in its base form!
Example:
- Do you like vegetables?
- Does she feel something with him? – we do not use „feels“
- Do they want fries?
Conjugation
As we know, we have to modify verbs into forms that serve our purpose. In affirmative sentences, it is necessary to add the suffix –s/-es/-ies to every verb with a subject in the 3rd person.
Suffix (-es)
The suffix –es is added to every verb that ends with -o, -ch, -sh, -s, -x, or –z.
The verb „go“ will turn into „goes“.
- Kiss –> Kisses
- Wash –> Washes
- Go –> Goes
Suffix (-ies)
The suffix (-ies) is added to every verb ending with a consonant + y. The last letter (Y) will be replaced with the suffix –ies.
- Carry –> Carries
- Study –> Studies
- Marry –> Marries
Suffix (-s)
The suffix –s is added to other cases not mentioned.
- Feel –> Feels
- Look –> Looks
- Play –> Plays