The present continuous tense is used for actions happening now or for an action that is unfinished.
The present continuous tense (sometimes referred to as the present progressive or present imperfect) is the verb tense most commonly used in modern English. It combines the present tense and continuous aspect.
This tense is really different from the present simple tense in its construction as well as in its use. While approximately 50% of spoken verbs are in the present simple tense, only 5% are in the present continuous tense.
Look at:
Construction of sentences
Construction of sentences in the present continuous is easy. The only thing you have to know is that you need to add the suffix – ing to the main verb in its base form and add the auxiliary verb „to be“ after the subject. First and foremost, we must know how to use the verb „to be“ depending on the subject.
The verb „to be“
The verb „to be“ is one of the most important verbs in the present continuous tense. Its irregular form (present tense) is used in every sentence using this tense. We know three forms of this verb in the present tense: Am, Are and Is.
Using irregular forms of the verb „to be“
The use of irregular forms of the verb „to be“ in the present continuous depends on the person of the subject. There are some rules to follow when using these forms.
Irregular form „am“
We use the form „am“ only in combination with the 1st person singular (I am). We can also use its short-form „ I’m“.
Example:
- I’m feeling really well.
- I am doing my homework right now.
Irregular form „is“
This form of the verb „to be“ is used in combination with the 3rd person singular only (he, she or it). We also very often use its short-form „‘s“, which includes an apostrophe.
The short-forms are as follows:
He is –> He’s, She is –> She’s, It is –> It’s
Example:
- He is sitting on his chair.
- She’s playing with her dolls.
- It is really interesting.
Irregular form „are“
We use this form for every other type of person, for instance when we talk about the 2nd person singular (you) or plural (we, they). Its short-form „’re“ can also be used instead (apostrophe included).
The short-forms are as follows:
We are –> We’re, You are –> You’re, They are –> They’re
Example:
- We are living in the UK.
- They’re waiting for my friend.
- You’re painting portraits really well!
Affirmative sentences in the present continuous tense
In affirmative sentences, we use the verb „to be“ in its present tense in combination with a verb and the suffix –ing. We have to distinguish between the person of the subject in every sentence to know how and when to use the correct form of the verb „to be“. We will only use the forms „am“, „is“ or „are“.
Once we know which form of the verb we have to use, we just add a verb with the –ing form.
The sentence will look as follows:
Subject + to be (am/is/are) + verb +(-ing) + object.
Example:
- I am washing all the dishes.
- She is watering the flowers in the garden.
- They are playing on the PlayStation.
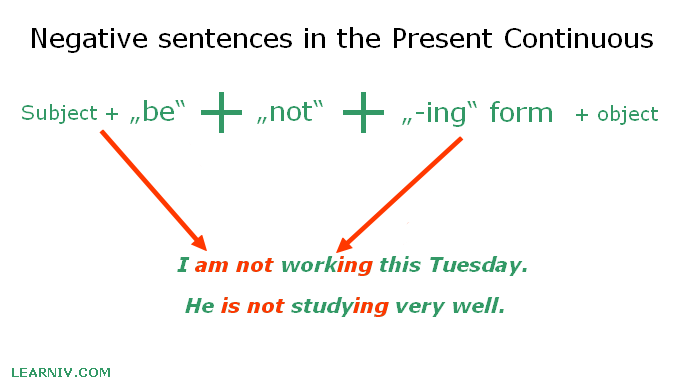
Negative sentences in the present continuous tense
To construct a negative sentence in this tense, we have to add the word „not“ after the auxiliary verb „to be“. If we want to describe the negative meaning, we must use the form „to be“ + not.
We must ensure we use the correct form of the verb „to be“. We can use any of the following forms:
| I am not / I’m not | We are not / We aren’t / We’re not |
| You are not / You aren’t / You’re not | You are not / You aren’t/ You’re not |
| He, she, it is not / He, she, it isn’t / He’s, she’s, it’s not | They are not / They aren’t / They’re not |
In formal conversations, we always use the full form as it is more polite. In non-formal conversations, we can use all short-forms.
The sentence will look as follows:
Subject + to be (am, are, is) + not + verb+(-ing) + object.
Example:
- I’m not working this Tuesday.
- They’re not having a good time.
- He is not studying very well.
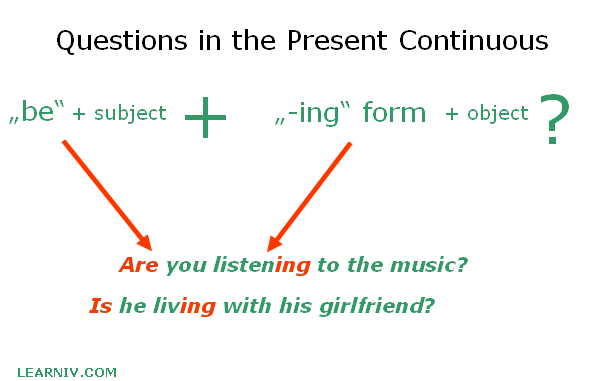
Questions
To construct a question we have to put the verb „to be“ at the beginning of the sentence, in front of the subject. The rest of the sentence is similar to that of an affirmative sentence. Again, we add the suffix –ing to the base form of the verb.
The sentence will look as follows:
To be (am, are, is) + subject + verb +(-ing) + object?
Example:
- Are you listening to music?
- Am I really that annoying?
- Is he living with his girlfriend?
When do we use the present continuous tense?
We use the present continuous tense on many occasions. As we know, this tense is used to talk about events and actions in the present. We just need to know when it is better to use the present simple or the continuous. We use the present continuous to talk about:
Something is happening right now
We use this tense to talk about something happening at the exact moment that we are speaking. Everything that is happening exactly at this moment can be described with the present continuous tense.
Example:
- He is doing his homework.
- I am laying in bed.
- My mom is cooking dinner right now.
Something happening in the present but not at the exact moment of speech
We use this tense to also talk about something that is happening in the present but just not during the exact moment of speech. We usually talk about something in the present that is true for a longer period of time.
Example:
- He is working in Budapest.
- He is studying in London.
Something changing and developing
We use this tense to describe that something is changing or developing. The change can be of growth, development, building or anything else.
Example:
- She is growing so fast!
- My English skills are improving.
Event planned in the near future
We can use the present continuous tense to talk about something planned in the future, but we have to ensure that we describe the exact timing of this event in the future.
Example:
- He is having an important meeting tomorrow at 5 o’clock.
- What are you doing next Monday?
Hyperbolic or ironic meaning of a sentence
We can also use the present continuous tense to exaggerate an action. We can use the adverbs „always“ or „never“ but we can actually mean them in opposite ways. We can also emphasize the frequency of the action in a humorous way.
Example:
- I’m never doing my homework last minute.
- My mum is always making me go to school!
- You are always eating a lollipop.
Temporary situations
We use the present continuous tense to speak about temporary conditions which are true in the moment that we are talking about them.
Example:
- She is using my car for now.
- I’m living with my father at the moment.
Something happening again and again
We can use the present continuous tense and even present simple in this instance as both tenses have a similar meaning in this particular context. As such, we can use the continuous tense for something that is happening repeatedly.
Example:
- It is never raining in Florida.
- Those two are always laughing.
Stative verbs
The only exception in the present continuous is stative verbs. We know we have to add the suffix – ing to every base word to form a continuous tense, but this is not the case with stative verbs. We cannot use stative verbs with any suffixes, so we must always use the present simple.
There are some exceptions. We can use some stative verbs in combination with the suffix –ing, but this is an exception. Typically, we cannot use them like we would with normal verbs.
Therefore, we use these verbs in their main and base form. We categorize stative verbs into:
Verbs describing thoughts and feelings
These verbs are:
| believe | dislike | prefer | realise | understand |
| like | know | remember | recognise | want |
| love | hate | suppose | think | wish |
Although we can use some of these verbs with the suffix –ing, the meaning of the final sentence will not make sense. As such, it’s best to use the present simple to be 100% certain that we are right.
Verbs of the senses
These verbs are:
| appear | smell | taste |
| look | feel | seem |
Others
There are many others stative verbs. Some of them are:
| belong | agree | own |
| be | owe | posses |
Since we cannot use stative verbs in the present continuous tense, we have to use the present simple. Whenever you want to use any of the stative verbs, make sure you use the present simple. You will not be wrong!
Example:
Wrong: This boy is agreeing with me.
Correct: This boy agrees with me.
Spelling verbs in the present continuous tense
We know we have to add the suffix –ing to the end of the verb. Usually, we just add this suffix and we are done, but there are some words which we have to change a little bit to ensure they are correct.
Sometimes we double the last letter while other times we change the letter completely. There are some rules which tell us how to create the continuous form of these verbs correctly.
Ending with a consonant + stressed vowel + consonant
If the base form of the verb ends with a consonant + stressed vowel + consonant, then we double the last letter. Vowels are a, e, i, o, u.
Example:
- Stop –> Stopping
- Run –> Running
- Begin –> Beginning
Ending with vowel + consonant + e
If the base form of the verb ends with vowel + consonant + e, then the „e“ is changing into „i“.
Example:
- Come –> Coming
- Mistake –> Mistaking
Ending with –ie
If the base verb ends with „ie“, than the „ie“ is changed into „y“.
Example:
- Lie –> Lyng
- Die –> Dying