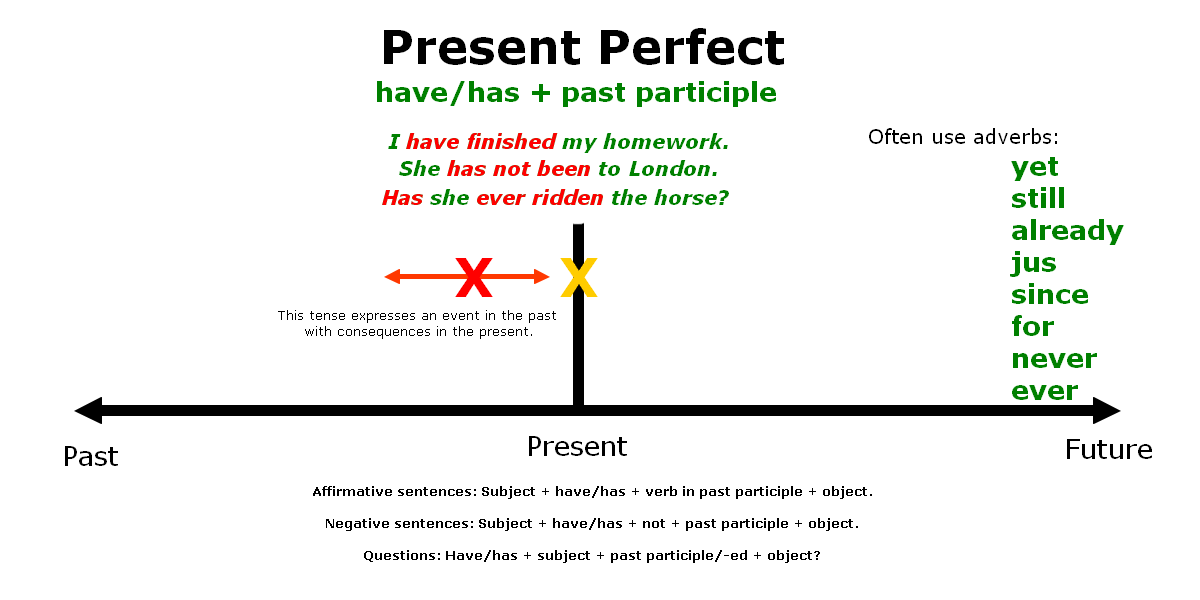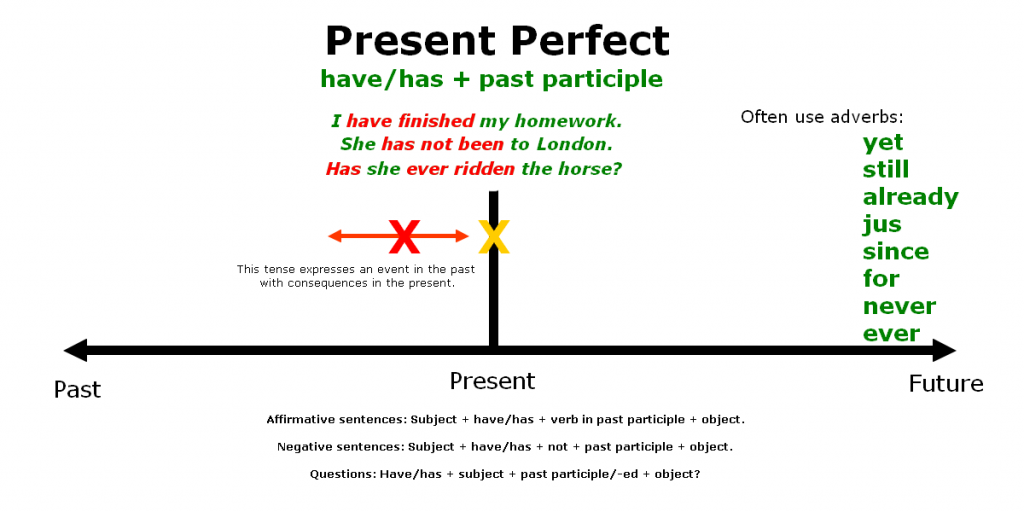
The Present Perfect tense is used in several situations:
- To talk about past actions or events with a present relevance: When the past action or event has a connection to the present moment or its effects are still felt, the Present Perfect is used. For example: “I have lost my keys” (the keys are still missing).
- To describe experiences: When discussing life experiences or accomplishments, the Present Perfect is used. For example: “I have traveled to many countries” (referring to a person’s travel experiences).
- To discuss recent past actions: When referring to actions that happened in the recent past without specifying a precise time, the Present Perfect is used. For example: “She has just finished her homework” (indicating a recently completed action).
- To express actions that have occurred multiple times: When talking about actions or events that have happened repeatedly up until the present moment, the Present Perfect is used. For example: “We have visited that museum several times” (indicating multiple visits in the past).
- With the words “never,” “ever,” “already,” and “yet”: These time expressions are commonly used with the Present Perfect to indicate experiences or actions up to the present moment. For example: “Have you ever been to Paris?” or “I haven’t finished reading the book yet.”
Overall, the Present Perfect tense is used to describe past actions or events that have a connection to the present, indicate experiences, discuss recent past actions, express repeated actions, or use specific time expressions.
Grammatical rules for the Present Perfect tense
The grammatical rules for the Present Perfect tense include the following:
- Formation: The Present Perfect tense is formed using the helping verb “have” (or “has” for the third-person singular) followed by the past participle of the main verb. For regular verbs, the past participle is formed by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb. However, irregular verbs have unique past participle forms. Examples:
-
- I have studied for the exam.
- She has eaten lunch already.
- Subject-Verb Agreement: The verb “have” changes its form based on the subject of the sentence. It is conjugated as follows:
- I, you, we, they: “have”
- He, she, it: “has”
Examples:
- They have visited the museum.
- He has completed his assignment.
- Time Expressions: The Present Perfect tense is often used with time expressions that indicate the time period up until the present moment. Common time expressions include “already,” “yet,” “just,” “recently,” “so far,” “ever,” and “never.” Examples:
- Have you finished your homework yet?
- She has already eaten breakfast.
- Negative Form: To form the negative form of the Present Perfect, “not” is added between “have/has” and the past participle of the verb. Examples:
- I have not seen that movie.
- They haven’t arrived yet
See other examples of negative sentences of Present perfect tense.
- Interrogative Form: In interrogative sentences, the auxiliary verb “have/has” is placed at the beginning of the sentence, followed by the subject, and then the past participle of the verb. Examples:
- Have you visited that place before?
- Has she finished her work?
See other examples of interrogative sentences of Present perfect tense.
- Use of “For” and “Since”: The Present Perfect is often used with the prepositions “for” and “since” to indicate the duration of an action or event. “For” is used to express a period of time, while “since” is used to indicate a specific starting point in time. Examples:
- She has been studying for three hours.
- I have known him since 2010.
It’s important to note that the Present Perfect tense is used to connect the past to the present, emphasizing the relevance of past actions or events to the current moment.
More examples of Present Perfect sentences
Other examples:
- 5 examples of sentences of Present Perfect tense
- 10 examples of sentences of Present Perfect tense
- 20 examples of sentences of Present Perfect tense
- 50 examples of sentences of Present Perfect tense
- Present Perfect irregular and regular verbs list