The past simple tense (sometimes called preterite, simple past or past indefinite) is the basic form of the past tense. This is one of the most common past tenses and can describe a lot of events. It is really important to know how and when to use this tense for daily conversation.
The term „simple“ is used because it distinguishes syntactic sentences from the auxiliary of the past perfect or past progressive tense. The past simple is one of the easiest tenses to learn, which is one reason why this tense is called the past simple tense.
Look at past simple tense examples or 10 examples of simple past tense.
When do we use the past simple tense?
The past simple tense is used to describe most events in the past. It is a very commonly used tense and it is really important to know how and when to use it.
Events in the past
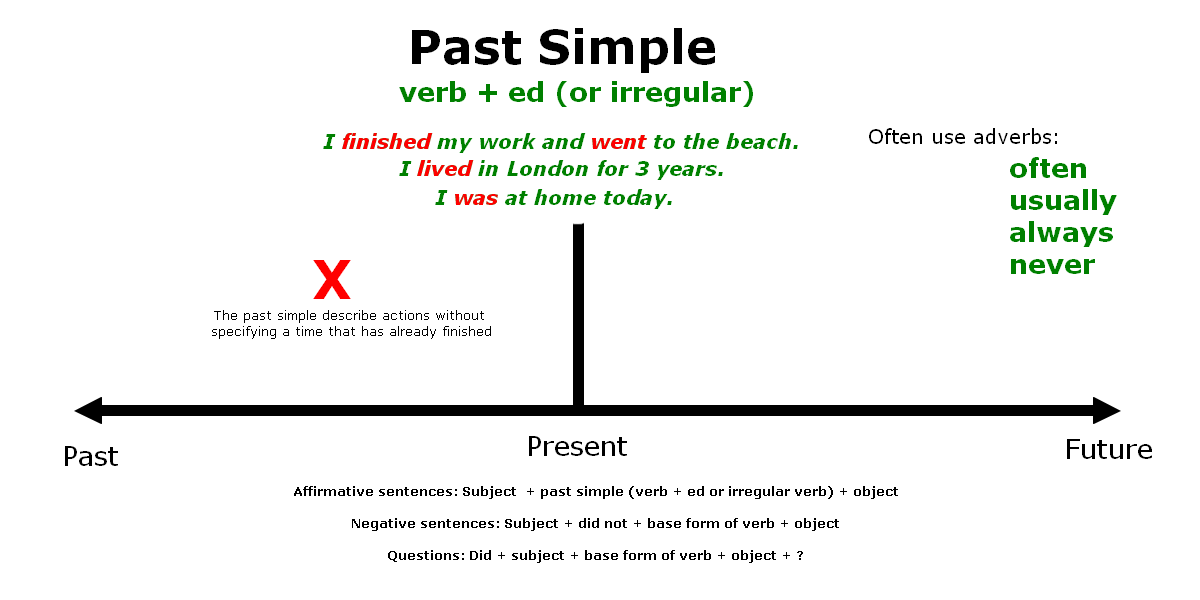
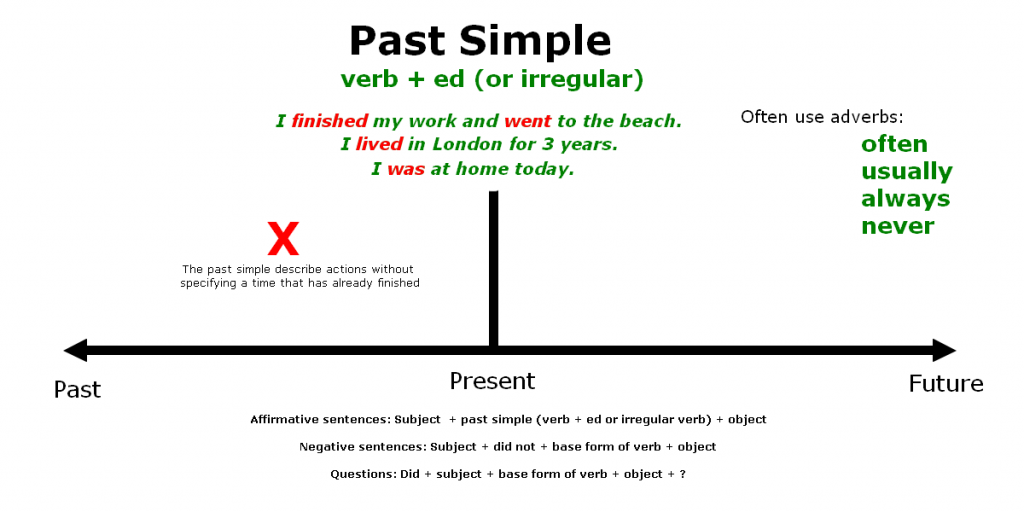
The past simple tense is used to describe actions without specifying a time, but we do have to be certain that the speaker is talking about an event that has already finished.
Example:
- I finished my work and went to the beach.
- I came home after lunch.
Finished events
We do not have to know when the event happened, we just need to be certain that the speaker is referring to a finished period of time.
This event could happen only once, or it can happen repeatedly. The past simple also describes events that have already ended and did not translate into the future. We use this tense to talk about something that was true for some time in the past.
Example:
- I saw this movie in a cinema last week.
- I was sick on Tuesday.
Habits
The past simple tense is also used to describe past habits. When referring to past habits, the use of the past simple has the same meaning as the expression „used to“. These types of sentences are often combined with expressions of time such as: „often“, „usually“, „always“ or „never“.
Example:
- I usually played tennis when I was in London.
Events that started and finished in the past
The past simple tense also describes events that happened in the past and lasted for a certain period of time, such as living abroad or some other action that lasted for a long time. These actions are specified by using time periods such as „the whole year“, „the whole week“ or „all day“.
Example:
- I lived in London for 3 years.
- I was in Alaska for the whole year.
- I worked on it all day long.
More examples of Past Simple sentences
more examples:
- Past simple affirmative negative and interrogative structure
- Past simple sentences
- 5 sentences of simple past tense
- 20 sentences of simple past tense
- 100 sentences of simple past tense
- Differences: Present Perfect and Past Simple
Construction of sentences
The past simple is one of the easiest tenses to construct. The only problem is that there are irregular verbs that we must keep in mind.
TIP: see examples of 5 sentences of simple past tense.
Affirmative sentences in the past simple tense
The affirmative past simple is composed of a verb in the 1st form (infinitive) in combination with the suffix –ed. However, in English there are a lot of irregular verbs which we cannot combine with –ed. These irregular verbs have their own forms which we have to memorize.
In the past simple we don’t differentiate between the person or number of subjects. We always use the past tense form no matter what. In contrast to the present simple tense where we differentiate between the specific person or number of subjects, in the past simple we only care about learning irregular verbs.
This means we do not add the suffix –s to the 3rd person singular as in the present simple but instead only add the suffix –ed to regular verbs.
As a result, this tense is actually much easier to use than the present simple, but only if we do not have to use any irregular verbs.
If we have a sentence with an irregular verb form then we must know its irregular past tense form, otherwise we are unable to construct a sentence.
The complete sentence would be as follows:
Subject + past simple (verb + ed or irregular verb) + object.
Examples:
- I played rugby yesterday.
- I saw my grandmother last week.
- I was in the hospital on Tuesday.
The Verb „to be“
The verb „to be“ is a special one in the past simple. If we want to describe the verb „to be“ in the past simple, we need to use its irregular form. In contrast to other verbs, this verb has two past tense forms – WAS or WERE.
Was
We use „was“ in sentences where the first or third person is singular, meaning we use it for subjects such as „I“ or „He, She, It“.
Were
„Were“ is used for subjects in other instances (You, We, They).
The verb „were“ is also often used to replace the verb „was“. It is very common in modern English, to find sentences that use „were“ instead of „was“ in combination with the subject „I“ even though it’s grammatically correct to use „I was“ instead.
„Were“ is also very often used to describe conditional causes.
Example:
- I was at home today.
- She was really happy.
- They were proud of her for finishing her exams.
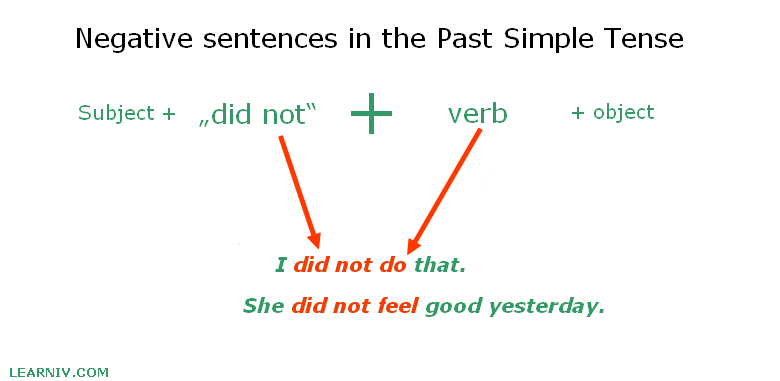
Negative sentences in the past simple tense
To describe the negative meaning of a sentence it is necessary to use the auxiliary verb „did not“ or its short form „didn’t“ in combination with the base form of the verb (infinitive).
The complete sentence would be as follows:
Subject + did not + base form of verb + object.
Example:
- I did not do that.
- They didn’t play basketball today.
- She did not feel good yesterday.
Negative sentences are really easy to construct. Pay attention – we never use negative (did not) with the past tense form (2nd form) of irregular verbs or in combination with verbs with the suffix –ed!
Example:
I didn’t played (play) football yesterday.
She did not went (go) to the theatre last month.
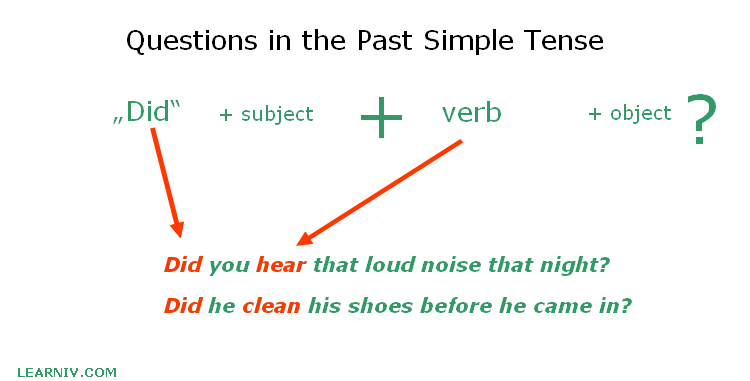
Questions in the past simple tense
To form a question in the past simple we need to use an auxiliary verb „did“ in front of the subject and the base form of the verb. „Did“ is the affirmative meaning of the verb „did not/didn’t“. „Did“ is also the 2nd form (past tense form) of the irregular verb „do“.
The complete sentence would be as follows:
Did + subject + base form of verb + object ?
Example:
- Did you hear that loud noise that night?
- Did he clean his shoes before he came in?
- Did they really do that?
TIP: We have prepared a complete list of irregular verbs in English. It contains more than 600 verbs, sorted by difficulty.
The verb „do“
Pay attention when using the irregular verb „do“ in the past simple. In the past simple, we have to use the verb „did“ to describe a question, but we must also use the verb „do“ in its base form. Therefore, the final sentence would be composed of two types of the verb „do“ – its base and past tense form.
Example:
- Did you that? – WRONG
- Did you do that? – RIGHT
We always need to use two verbs. One is „did“ and the other is the basic form of the chosen verb. There are no exceptions for the verb „do“.
Conditional and dependent sentences in the past simple
Conditional and dependent sentences are very often used in English. They describe events that happened in the past and had there been changes to any of these events, the outcome would have been different.
Example:
- If he walked faster, he would get to his job on time.
- If I knew it, I wouldn’t do
- I wish I read this book before it happened.
We can also combine two or more verbs in the past tense form as there is no rule for every sentence to have only one verb in the past tense form.
Example:
- He said he wanted to go to the theatre.
- She felt it and knew it was benzene.
Pronunciation
The pronunciation of irregular verbs is really important to know. Many irregular verbs have the same written form of a verb but different pronunciations. That‘s the main reason why we need to memorize them really well.
Regular verbs have one simple pronunciation rule:
- Verbs ending with voiced consonants are pronounced as /d/
- Verbs ending with unvoiced consonants are pronounced as /t/