The future perfect continuous expresses the duration of activities that extend until a certain point in time in the future. While this tense is hardly ever used in spoken English, it is still useful to know and understand it.
For a basic understanding of how this tense works, you need to be familiar with two very similar tenses: the past perfect continuous and the present perfect continuous. Both of these tenses are formed in the same way as the future perfect continuous tense.
Look at the future perfect continuous tense examples.
Sentence structures
As with the past perfect continuous and present perfect continuous tenses, we form the continuous aspect by ending the verb with the suffix -ing.
This tense has two different forms: the first with the verb WILL and the second with the verb GOING TO. However, unlike the future simple tense, it does not matter when we use which form. It is therefore possible to freely choose the verb that works better for us without worrying about changing the meaning of the sentence.
With the verb WILL
The first way to express this tense is by using the verb WILL.
To construct a sentence in the future perfect continuous tense, we first need to add the auxiliary verb HAVE in its original form to the verb WILL, which represents the future tense.
The verb “to be” in its past participle form is then added to both of these verbs – that is, in the form BEEN. Finally, we add the main verb with the suffix -ing.
The sentence structure in the future perfect continuous tense with the verb WILL is:
Will + have + been + verb (-ing).
With the verb GOING TO
The second form of the future perfect continuous tense uses the verb GOING TO, which, like the verb WILL, represents the future tense.
With the verb “going to” we must never forget the verb “to be”, whose form depends on the number and person of the pronoun used (am, is, are).
Here too, we add the auxiliary verbs HAVE and BEEN in combination with the main verb with the suffix -ing.
The sentence structure using the verb GOING TO looks like this:
Am/Is/Are + going to + have + been + verb (-ing).
The use of the future perfect continuous tense
The future perfect continuous tense speaks of situations or events that are not yet completed but which we know will be completed in the future.
The adjective “continuous” tells us that an event in the future will have some duration – it will run its course.
This tense is always accompanied by a defined length of time, so we always know when the event will take place or how long it will last.
Since we make no distinction as to whether to use the form with the verb WILL or with the verb GOING TO, there is no need to differentiate between the uses of the tense.
The termination of an event at some point in the future
The future perfect continuous tense is used to express events that will be completed before or at some point in the future. If we know that an event will take place and have a duration up to a certain point, we use this tense.
It is usually associated with adverbs such as “for 30 minutes”, “for 2 weeks”, or “since Friday”.
These are the periods of time that usually end the event. Such a period of time can also be another event in the future that will take place in parallel.
Example:
- We will have been watching TV for an hour by the time he comes.
- He is going to have been talking to her until the movie starts.
- I will have been waiting there for 5 hours when my train finally arrives.
- How long are you going to have been studying when you graduate?
Causes
Another example where this tense is used is to indicate causes in the past that led to a consequence in the future. By using the future perfect continuous past tense, we can announce these causes.
Example:
- They will be very surprised when they come home because we will have been preparing the b-day party!
- Her cooking skills are going to be perfect when she returns to London because she will have been studying at a culinary school in Berlin.
- I will be really fit when she comes because I will have been working out for 3 months!
- I will be really tired when I come because I am going to have been working for 16 hours tomorrow.
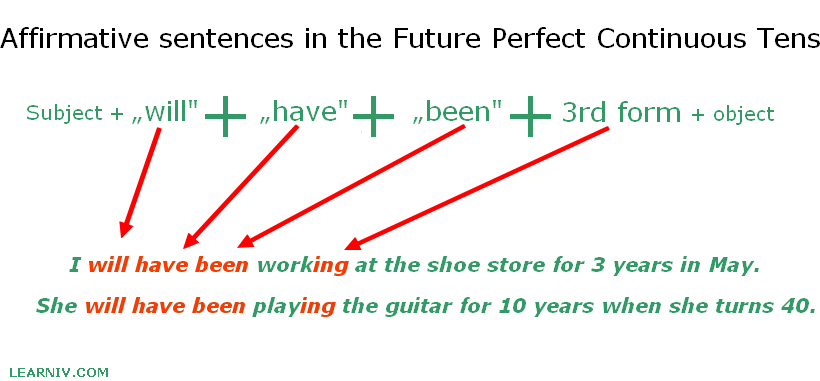
Affirmative sentences
Affirmative sentences are formed using three basic verbs. These are the verbs WILL or GOING TO, the verb HAVE as well as the verb BEEN. These are followed by the main verb with the suffix -ing.
The sentence structure with the verb WILL would therefore be:
Subject + will + have + been + verb (-ing) + object.
Example:
- I will have been working at the shoe store for 3 years in May.
- She will have been playing the guitar for 10 years when she turns 40.
With the verb GOING TO:
Subject + to be + going to + have + been + verb (-ing) + object.
Example:
- After 2 minutes they are going to have been waiting for the train for 40 minutes.
- By 2008, she is going to have been living there for 13 years.
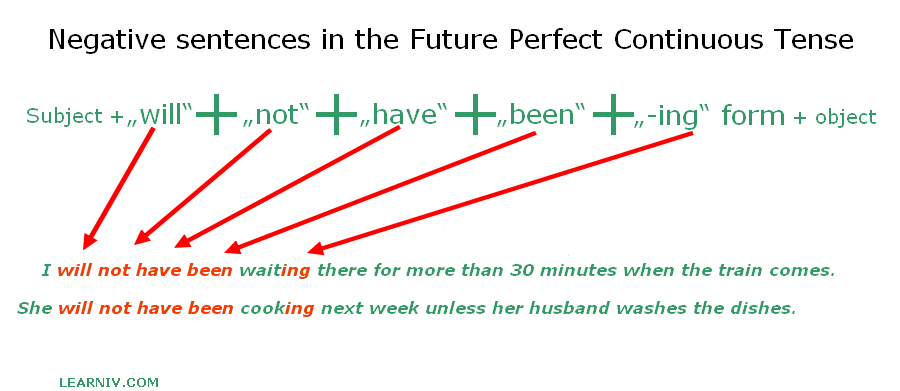
Negative sentences
The only way to form negative sentences is to add a negative in the form of “not” to both the verb WILL and the verb GOING TO, changing these to “will not/won’t” or “not going to”, respectively.
The negative sentence structure with the verb WILL is:
Subject + will + not + have + been + verb (-ing) + object.
Example:
- I will not have been waiting there for more than 30 minutes when the train comes.
- She won’t have been cooking next week unless her husband washes the dishes.
With the verb GOING TO:
Subject + to be + going to + have + been + verb (-ing) + object.
Example:
- I am not going to have been living in the UK for another 5 years when I come back.
- She isn’t going to have been learning English for 3 years when she finishes this course.
Questions
The creation of questions in the future perfect continuous tense is the same as in the other tenses. It is simply a change in word order where we put the auxiliary verbs WILL and possibly GOING TO at the beginning of the sentence, followed by the subject and the rest of the sentence.
The structure of a question with the verb WILL is:
Will + subject + have + been + verb (-ing) + object?
Example:
- When she comes at 4:00 PM, will you have been playing the piano?
- It is 10 years you live there. Will you have been living there for the next 10 years?
With the verb GOING TO:
To be + subject + going to + have + been + verb (-ing) + object?
Example:
- Am I going to have been working there for the next 3 years after such a long time?
- When I come, are you going to have been practising English?
Where to put the adverbs
Placing adverbs correctly in long sentences such as ones with the future perfect continuous tense is often very hard. Here we are referring to adverbs like “always”, “only”, “never”, “ever”, “still” or “just”. The following examples highlight the different placement of the adverb “only” depending on the sentence:
Example:
- I will ONLY have been waiting for 5 minutes when the bus comes.
- I’m ONLY going to have been waiting for 5 minutes when the bus comes.
- Will I ONLY have been waiting for 5 minutes when the bus comes?
- Am I ONLY going to have been waiting for 5 minutes when the bus comes?
The active vs. the passive voice in the future perfect continuous tense
The active and the passive in the future perfect continuous tense cause many people minor problems. Fortunately, it is not that difficult.
If you can handle the past tense in English, it shouldn’t be too difficult to learn the future perfect continuous tense using the passive voice. As with the active voice, we’ll use the form “will have been + verb -ing”.
To achieve the final passive form, we will need to add the verb “being” to the sentence and express the main verb in the 3rd form – that is, the past participle.
The sentence structure with the verb WILL is:
Will + have + been + being + past participle
If we use the verb GOING TO, we will use:
(am, is, are) + going to + have + been + being + past participle
Example:
- The book will have been being written by my mom.
- The book is going to have been being written by my mom.
- My old house will have been being renovated by the construction company for over 5 months until it is done.
- My old house is going to have been being renovated by the construction company for over 5 months until it is done.